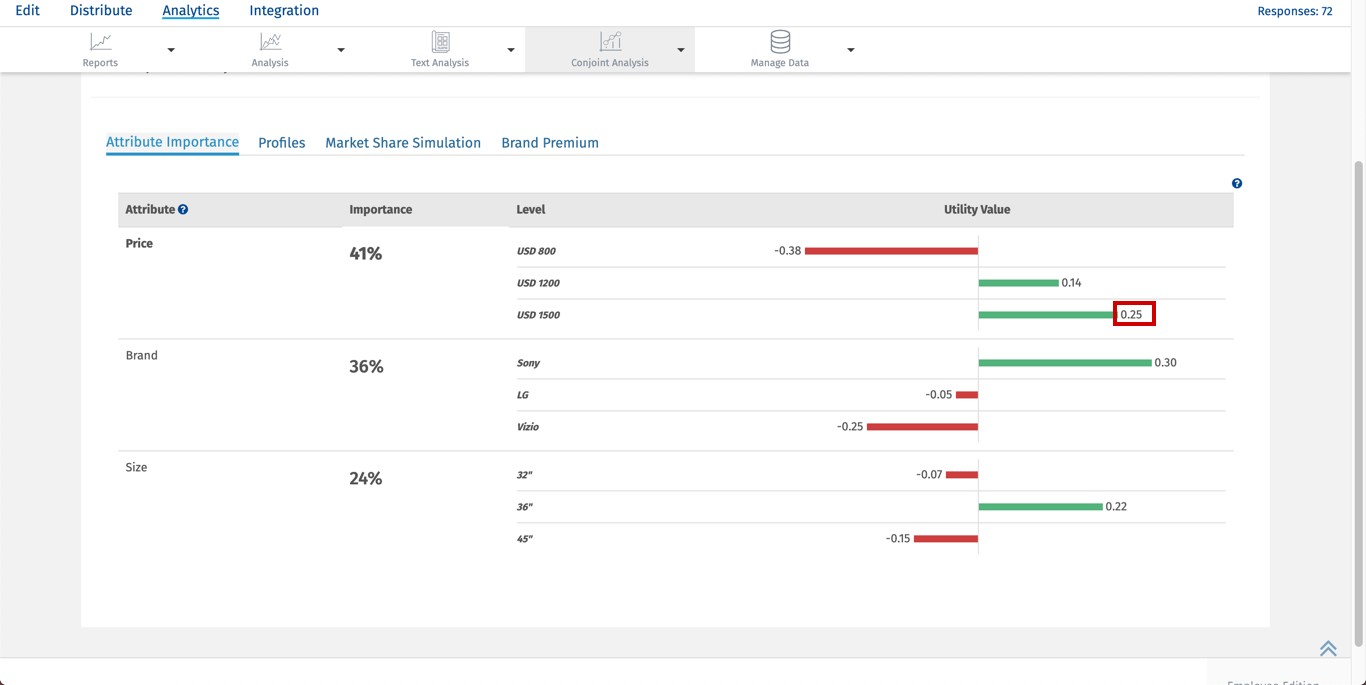
Conjoint Analysis – Attribute Importance
Attribute Importance is also known as Relative Importance, this shows which attributes of a product or service are more or less important when making a purchasing decision.
To view detailed Attribute Importance:
Go to: Login » Surveys » Reports » Choice Modelling » Conjoint Analysis » Attribute Importance
Calculating Attribute Importance
Sometimes we want to characterize the relative importance of each attribute. We can do this by considering how much difference each attribute could make in the total utility of a product. That difference is the range in the attribute’s utility values.
Importance measures are ratio-scaled,but they are also relative,study-specific measures. An attribute with an importance of twenty percent is twice as important as an attribute with an importance of ten, given the set of attributes and levels used in the study. That is to say, importance has a meaningful zero point,as do all percentages. But when we compute an attribute’s importance,it is always relative to the other attributes being used in the study. And we can compare one attribute to another in terms of importance within a conjoint study but not across studies featuring different attribute lists.
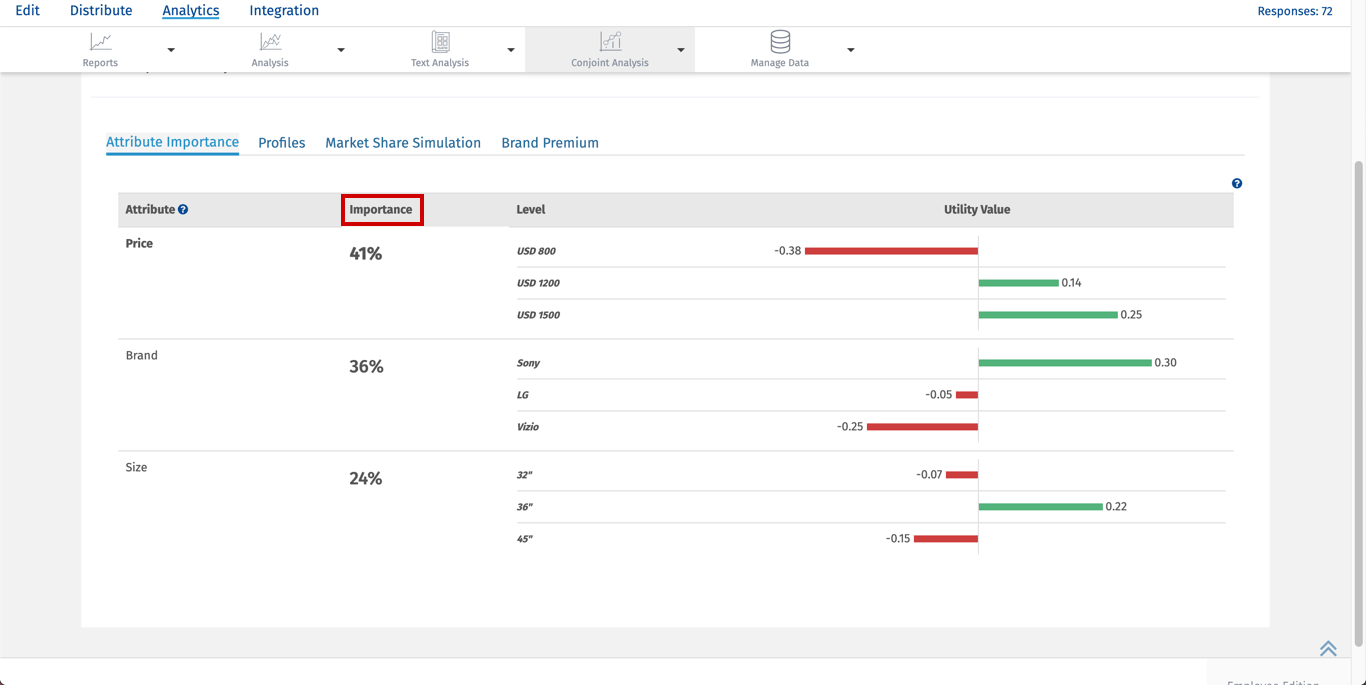
Example:
Step 1: Calculate Attribute Utility Range
Utility Range = Highest Utility Value of an attribute - Lowest Utility Value of an attributeFor Price Range is calculated as 0.25-(-0.38) = 0.63
For Size Range is calculated as 0.30-(-0.25) = 0.55
For Brand Rage is calculated as 0.22-(-0.15) = 0.37
Step 2 : Calculate Total Attribute Utility Range
Total Utility Range = ∑ Utility RangeTotal Attribute Utility Range = 0.63+0.55+0.37 = 1.55
Step 3: Calculating Relative Importance of attributes
Relative Importance of attribute = (Attribute Utility Range/Total Attribute Utility Range)*100Importance of Price = (0.63/1.55)*100 = 40.64% Rounded off to 41%
Importance of Size = (0.55/1.55)*100 = 35.48% Rounded off to 36%
Importance of Brand = (0.37/1.55)*100 =23.87% Rounded off to 24%
Calculating Utility Value
Conjoint utilities or part-worths are scaled to an arbitrary additive constant within each attribute and are interval data. The arbitrary origin of the scaling within each attribute results from dummy coding in the design matrix. We could add a constant to the part-worths for all levels of an attribute or to all attribute levels in the study, and it would not change our interpretation of the findings. When using a specific kind of dummy coding called effects coding, utilities are scaled to sum to zero within each attribute.
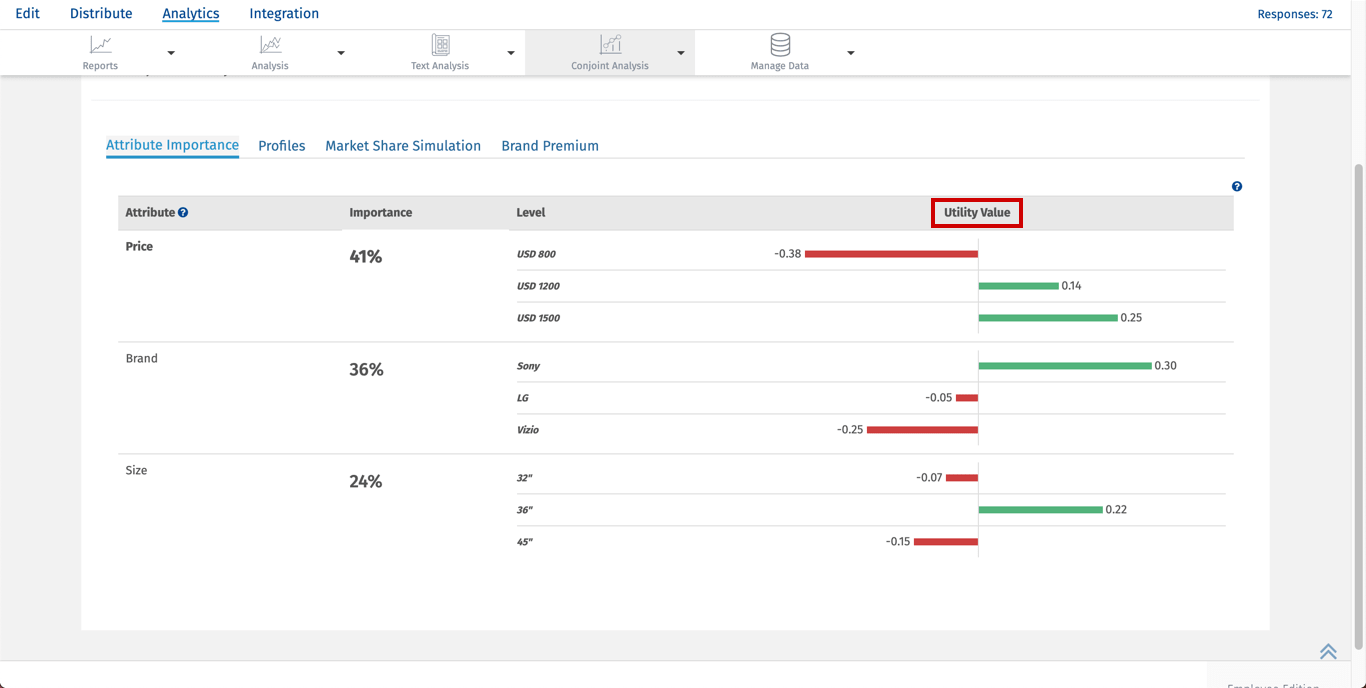
Utility Value is calculated using part worth value. For every level of attribute summation of part worth is calculated. Then the average of the summation is taken to get the utility value of a particular level.
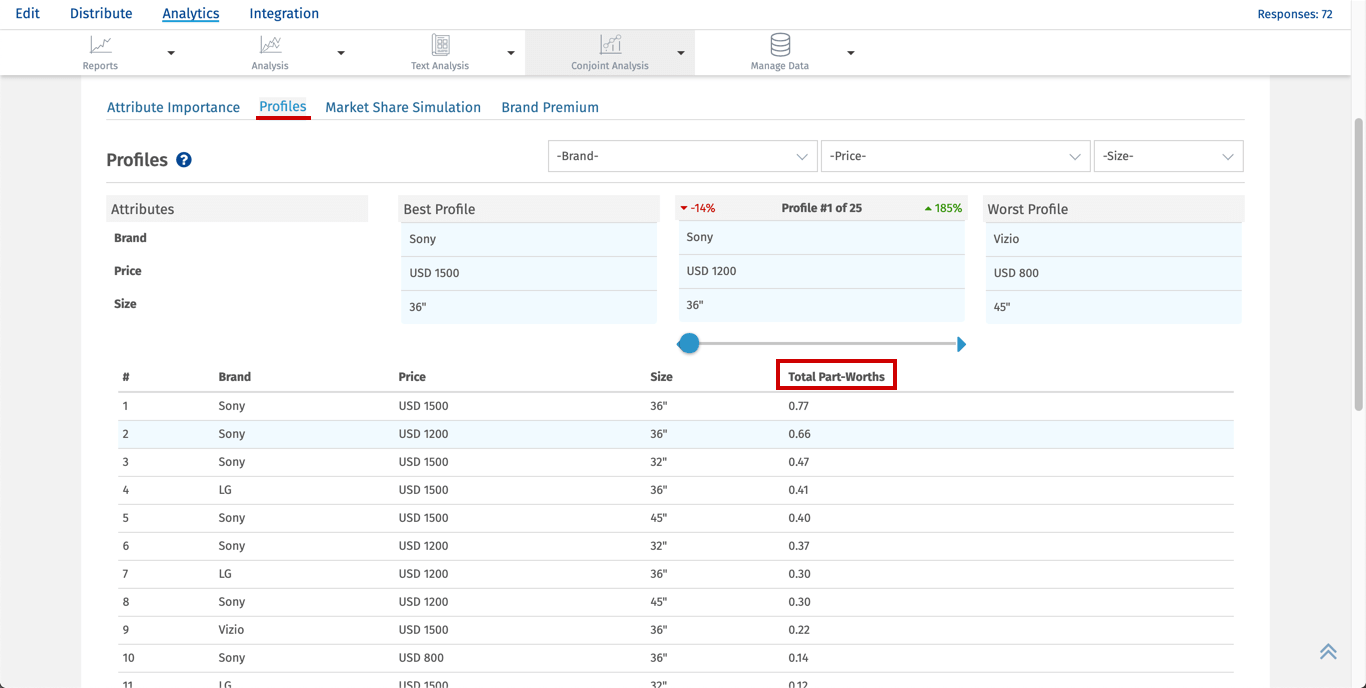
Example: Utility value for USD 1500 is calculated by taking summation of Total part worths for USD 1500 average of which will give utility value.
Summation of total part worths of USD 1500 = 0.77+0.47+0.40+0.41+0.22+0.12+0.05+(-0.08)+(-0.15)=2.21
Average = 2.21/9 which gives utility value of 0.25 for attribute price USD 1500